
Start the Disk Utility.app and unmount (don’t eject) the drive.Īnd remove your flash media when the command completesġ2. If you see the error dd: /dev/diskN: Resource busy, make sure the disk is not in use.Use the same command but replace bs=1m with bs=1M. If you see the error dd: Invalid number ‘1m’, you are using GNU dd.ubuntu.dmg).ġ0.Using /dev/rdisk instead of /dev/disk may be faster. (replace /path/to/downloaded.img with the path where the image file is located for example. Sudo dd if=/path/to/downloaded.img of=/dev/diskN bs=1m (replace N with the disk number from the last command in the previous example, N would be 2) dmg ending on the output file automatically.Īgain and determine the device node assigned to your flash media (e.g. Hdiutil convert -format UDRW -o ~/path/to/target.img ~/path/to/ubuntu.isoĤ.Note: OS X tends to put the. img using the convert option of hdiutil (e.g.,
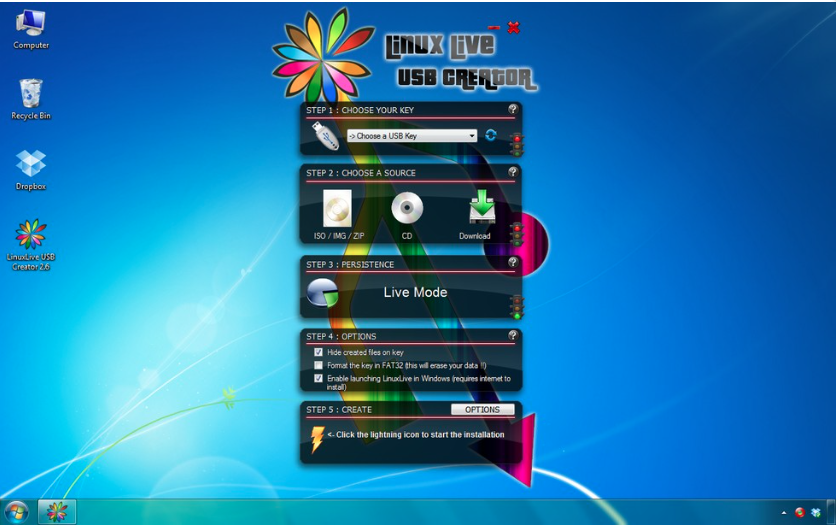
img file that you will be needed to create from the.
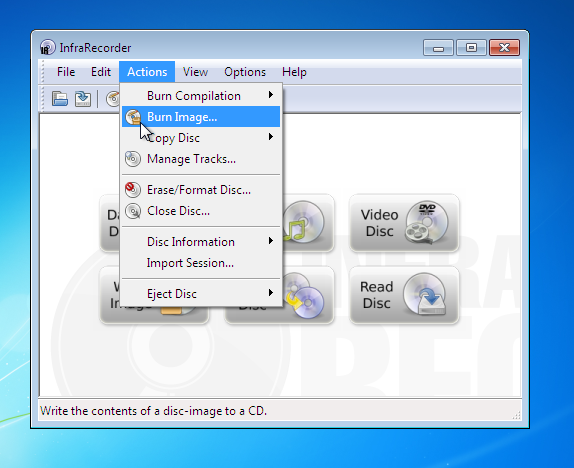
But if you would prefer to use a USB, please follow the instructions below. We would encourage Mac users to download Ubuntu Desktop Edition by burning a CD for the time being. If attempting to make a USB drive that can be booted from a Mac, follow the instructions below. The resulting USB drive, however, can be booted on PCs only.
#Burn ubuntu iso to usb mac for mac os x
UNetbootin for Mac OS X can be used to computerize the process of extracting the Ubuntu ISO file to USB, and making the USB drive bootable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
